Video Review
Key Concept Summary
TA Summary
True/False
If an object is at rest, no forces are acting on it.
Analysis
A ball is thrown straight up. Disregarding effects from the air, the forces acting on the ball from the time it leaves his hand until it returns to the ground are:
A beach ball rolls at constant speed across a smooth table top. Which of the following forces act on the ball as it rolls? (Select all correct answers.)
A ball is thrown horizontally. While it is in the air after being thrown, which of the following forces act on the ball? (Select all correct answers.)
Two masses are suspended, one on each side, from a pulley as shown. What direction is the force the rope exerts on the pulley? 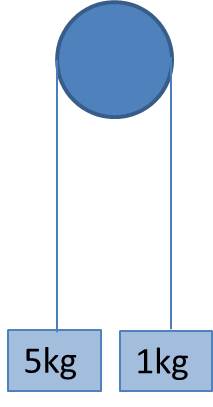

When traffic lights are suspended from a cable stretched across the street, the cables holding traffic lights sags. If enough tension were applied to the cable, could the cable ever be made perfectly straight?
What direction does friction point?
A book is at rest on a table on the Earth. Which which of the following forces must be acting on the book? (Select all correct answers.)
You slam on the brakes and your car starts to slow down. What direction is the net force exerted on the car as it slows?
A boat is headed across a river. The motor on the boat exerts a large force due north. The river current exerts a small force due east. The net force on the boat most nearly points which direction?
In an accident, a car collides with a semi-truck. Which of the following is true?
A sparrow and a charging rhinoceros experience a head-on collision. Which of the following is correct?
A large box is being pushed straight across the floor at a constant speed. What can you conclude about the forces acting on the box?
A man is standing on the ground. Which of the following pairs of forces acting on the man is an action-reaction pair as described by Newton's third law?
A police officer warns you that in a traffic accident an occupant of the front seat of a car can be "thrown" through the windshield if he is not wearing a seat belt. Which of the following is a correct explanation for what the officer is describing?
A car is going down a hill. The car is speeding up, so the driver of the car applies the brakes. He brakes just hard enough so that the frictional forces exactly equal the force that was accelerating the car down the hill. What happens?
A car is accelerating to the right. What direction is the frictional force on the car's tires from the ground?
Newton's second law deals with the rate of change of which of the following quantities?
A tow truck is towing a small car at a steadily increasing speed. What is true about the forces between the two?
A box is being pushed across a flat horizontal surface at constant speed. When the person applying the forward force stops pushing on it, what happens?
Suppose you see an object moving in a circle at constant speed. What can you say for sure about the force or forces acting on it?
Why does a passenger in a turning car feel thrown sideways as the car turns?
A ball is tossed straight up and caught by a passenger in a car moving at a constant velocity. Which of the paths in the diagram below best represents the path of a ball as seen by someone on the ground? 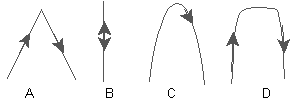

In which of the following situations will the speed of an object increase?
For an object moving in a circle at constant speed the acceleration of the object is:
When you are on a ferris wheel, you feel like you weigh less at the top and like you weigh more at the bottom. Why?
If you apply exactly the same net force to a 5 lb and a 10 lb dumbell, what will happen?
In which of the following situations will the speed of a car remain constant?
A car is traveling in a circle at constant speed. What can you conclude about the forces on the car.
A 130 lb girl stands in an elevator on a scale as the elevator just begins to move upward from the first to second floor. Which choice could properly describe her weight, contact force, and acceleration at this instant?
Now the elevator and the girl standing on the scale are mid-floor and are moving at a constant speed upward. Which choice could properly describe her weight, contact force, and acceleration at this point?
As the elevator approaches the second floor, it begins to slow to a stop. Which choice properly describes her weight, contact force, and acceleration at this point?
A bullet is fired horizontally from a high-powered rifle. At the same time, a second bullet is simply dropped from the same height as the bullet which was fired from the rifle. Neglecting air resistance, which statement is true about the acceleration of the first bullet after it leaves the gun compared to that of the second bullet as it falls?
A raindrop, as it falls to the ground, reaches a speed known as terminal velocity where the speed of the raindrop is neither increasing nor decreasing. This motion of the raindrop at terminal velocity can be understood in terms of:
Instructions for the next four questions
In the picture below, a boy on a sled is stopped at the top of a gentle hill. He starts down the hill, sleds at a constant speed for a short time, then slows down and stops at the bottom. In the following questions, you are asked to describe what is happening at various points along his path.
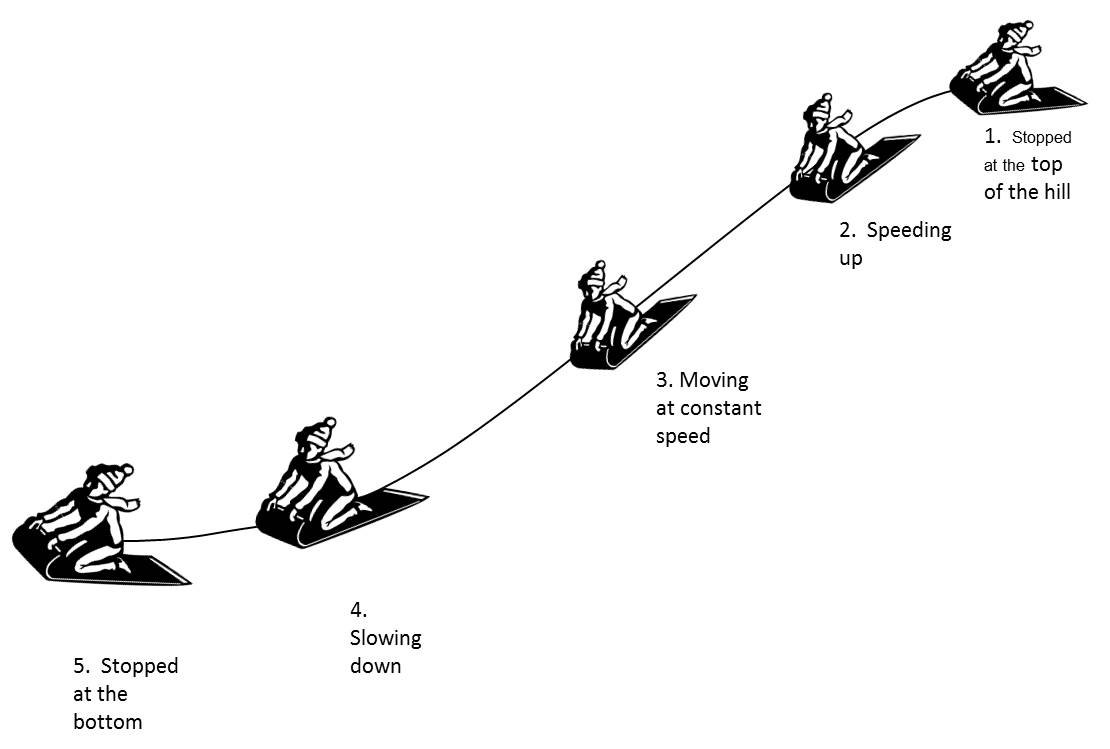
When would the boy's acceleration be directed backwards (opposite the direction he is moving)?
When would the boy's acceleration be directed forwards (in the same direction he is moving)?
Which of the following best explains what happens at the bottom of the hill?
At which of the points listed below would the net force on the sled be zero?
The boy and the sled exert forces on each other. When would the contact force the sled exerts on the boy be equal to the contact force the boy exerts on the sled?
A cannonball is shot horizontally from a cannon. At the same time a marble is dropped from the same height as the cannon. Which object will hit the ground first? (neglect air resistance)
Raindrops fall for several seconds, sometimes minutes, before reaching the ground. Why don't they strike the earth with speeds reaching hundreds of kilometers per hour?
Two metal balls are the same size, but one weighs twice as much as the other. The balls are dropped from the top of a two story building at the same instant of time. The time it takes the balls to reach the ground below will be:
Three identical balls are thrown at the same time, one is thrown upward, one horizontally, the other downward. Which will hit the ground first?
A loose wheel falls off of an airplane as it is in level horizontal flight from left to right. As seen from the ground, which path would the wheel most closely follow after leaving the plane? 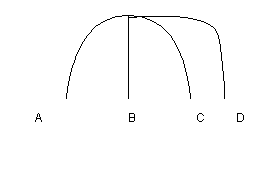

According to the universal law of gravitation which of the following is correct?
How does the sun's gravitational pull on the moon compare to its pull on the Earth?
Suppose we could send a manned mission to a distant asteroid about a mile in diameter. When the astronauts stepped out onto the surface of the asteroid what would they discover about their weight?
A man jumps out of an airplane, falls for a while and then opens his parachute. After a short time, he is falling with constant speed straight down. What forces are acting on the man as he falls with constant speed?
What is a centripetal force?
A satellite is moving around the earth with constant speed in a nearly circular orbit. What forces are acting on the satellite?
An object is initially moving under the influence of gravity. How does air friction change the acceleration of this object as the object increases in speed?
According to the course material, what is the suggested procedure to analyze forces on an object?
You would weigh slightly less standing on the top of mount Everest than you do on the beach. Why?
Free Response
First Law
- Provide an example of an object at rest that is experiencing no forces.
- Provide an example of an object in uniform motion that is experiencing no forces.
- Provide an example of an object at rest that is experiencing two or more forces. What forces act on the object? How do their sizes compare?
- Provide an example of an object in uniform motion that is experiencing two or more forces. What forces act on the object? How do their sizes compare?
- Why doesn't the First Law apply to an object experiencing a single force?
- Do the First and Second Laws of Motion ever apply to the same object at the same time? Explain.
Second Law
- Provide two examples of an object experiencing an unbalanced force in the direction it is moving. What do these objects have in common?
- Provide two examples of an object experiencing an unbalanced force opposite the direction it is moving. What do these objects have in common?
- Provide two examples of an object experiencing an unbalanced force perpendicular to the direction it is moving. What do these objects have in common?
- Give two examples of an object with zero velocity that is accelerating.
- Give two examples of an object accelerating while moving at constant speed.
- How many forces are acting on the moon? What is causing these forces? Why does the moon move around its orbit? Why doesn't it hit Earth?
- If you have 2 balls, a 1kg ball and a 2kg ball, and you push on them with the exact same force, how do the accelerations compare? Why?
- Because all objects near the surface of Earth experience the same gravitational acceleration when dropped, does this mean that they are experiencing the same gravitational force? Why or why not?
- On Earth, people often exercise by playing catch with a medicine ball (an extremely heavy ball). Would the same exercise work on a space station? Why or why not?
- In science, the word "weight" means the gravitational force acting on an object. Using this definition, are objects in orbit around Earth weightless? Explain your answer.
Third Law
- When a book is at rest on a table, its weight and the contact force from the table are equal and opposite. Are these forces an action-reaction pair? Explain your answer.
- 10-year-old Brianna challenges her 4-year-old sister Lindsey to an arm wrestling match. Brianna wins without trouble. How is this possible if Lindsay pushes on Brianna as hard as Brianna pushes on Lindsey?
- The BYU Society of Physics Students (SPS) challenges the BYU football team to a tug of war, with the one condition: that the SPS get to pick the playing field. The football team accepts, and the SPS announce that the match will take place at the Seven Peaks Ice Arena with the football team on the ice and the physics students standing on the concrete in the entrance to the rink. The SPS will try to pull the football players off the ice onto the concrete, and the football players try to pull the SPS off the concrete onto the ice. The first team to have a player touch the boundary between ice and concrete wins. Use Newton's Second and Third Laws to explain the strategy of the SPS.