Video Review
Key Concept Summary
TA Summary
Vocabulary
Depends on an object's position.
Depends on the position and motion of the object on the atomic scale.
Weight times height.
Depends on the position and motion of the whole object.
Moving an object in the direction of an applied force.
Something that keeps moving forever without any energy being added.
Depends on an object's motion.
Energy transfered through direct contact.
Heat is transferred when the hot material moves around.
Direct transfer of heat from one place to another without any need for intervening matter.
Energy associated with chemical bonds.
Depends on the position of atoms and molecules.
Depends on the position of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
True/False
Speed plays a more significant role than mass in determining an object's kinetic energy.
Gravitational potential energy decreases as the distance between two objects increases.
If an object remains stationary then no work is being done on it.
In the process of conduction, both matter and energy are exchanged.
The closer the protons and neutrons are to each other, the lower the nuclear potential energy.
Mass and energy are really two ways of measuring the same thing.
The heat you feel on your face from a campfire when the surrounding air is cold is an example of radiation.
Analysis
Energy can be defined as
If you move two positively charged objects closer together, then electrical potential energy
Two objects with opposite charges are brought closer together. Electrical potential energy
As you dribble a basketball, which of the following quantities is/are conserved?
If an object has kinetic energy, then it must be
Work is always done on an object when
"Pair production" demonstrates which of the following?
If two objects in uniform motion have the same mass but one is traveling faster than the other, which of the following statements is true?
When a skier glides down a ski slope:
When a ball is given a push and allowed to roll across a carpet, it will eventually slow to a stop. Why does it do this?
Kinetic energy depends on which of the following?
The next two questions refer to the diagram below. In the pictures four identical blocks are released from the same height at the same time shown. One is dropped straight down. The other three slide down frictionless slides in the shapes shown. 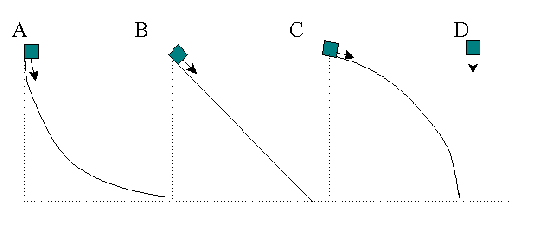
Which block has the largest speed at the bottom?
Which block has the largest kinetic energy at the bottom?
For the next two questions you will be comparing the motion of a box pushed across the floor of a carpeted room at constant speed to the motion of the same box carried across the room at the same constant speed.
How does the horizontal force you apply to the pushed box compare to the horizontal force you apply to the carried box.?
How does the work you do on the pushed box compare to the work you do on the carried box?
How does the total work done on the pushed box compare to the total work done on the carried box?
Which of the following statements about the sign of potential and kinetic energies is true.
A ball is rolling along the highway. From this information you know that
A skydiver is parachuting towards the ground. From this information, which of the following must be true?
You sit on a hot stove. Energy is transferred into your seat by the process of
A pendulum is swinging back and forth without any friction in the system. The next two questions deal with this pendulum. 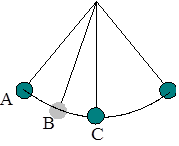
Which of the following quantities is conserved?
Where is the kinetic energy of the pendulum the largest?
Which one of the following statements is true?
Which one of the following statements is true?
Suppose an object is moving away from you with a speed near the speed of light. Which of the following choices is true?
A mass on a spring is bouncing up and down. Which of the following are conserved?
A rock is sitting on top of a hill. What type of energy does the rock have by virtue of its position?
Which of the following describes electrical potential energy
Which of the following describes thermal energy
If an object has kinetic energy, then it must
The pictures show the position of a car at equal time intervals. In which of the pictures below is the kinetic energy of the car increasing? 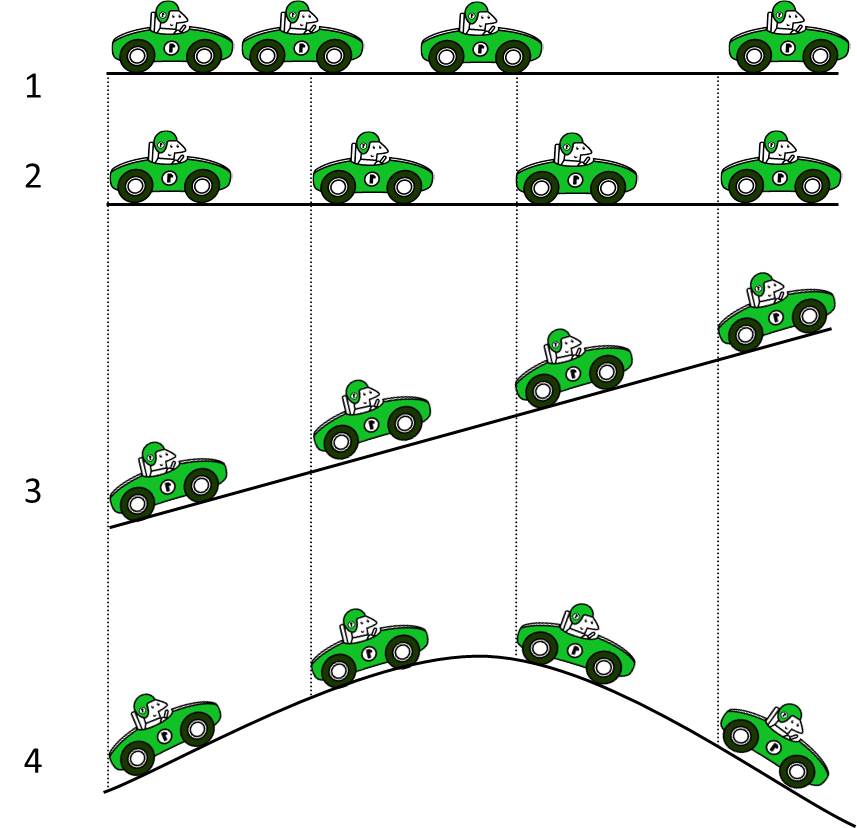

Free Response
- Name two examples of objects with elastic potential energy.
- What is the speed limit of the Universe?
- What is meant by the conservation of mass- energy?
- What are two consequences of mass- energy equivalence?
- Describe the important energy transfer and transformation mechanisms (work, conduction, radiation, and convection).
- Air and dynamite contain many of the same elements. What makes dynamite so much more destructive than air?
- Describe the energy changes that occur when an athlete pole-vaults, beginning with the athlete eating breakfast and ending after the athlete hits the mat.
- You walk into a computer lab and see many students doing homework. However, based on what you learned in Physical Science, you conclude that no one is really doing much "work" at all. What leads you to this conclusion?
- You accidentally drop your cell phone off a balcony. You know that the only thing that could possibly console you would be to examine the tragedy using your understanding of Physical Science.
- What kind(s) of energy does the phone have before it falls?
- What kind(s) of energy does it lose as it falls?
- What kind(s) of energy does it gain as it falls?
- What kind(s) of energy does it have just after it hits the ground and stops?
- How does the total amount of energy the phone has before it falls compare with the total amount of energy the phone has after it hits the ground and stops? How do you know?
- A frictionless pendulum is set in motion.
- What kind of energy does it have at the highest point of its swing?
- What kind of energy does it gain as it swings downward?
- As it swings upward again, what kind of energy does it lose? What kind does it gain?
- How does the conservation of energy apply to this situation?
- Now consider a real pendulum (with friction).
- What kind of energy does it have at the highest point of its swing?
- What kind of energy does it gain as it swings downward?
- As time passes, what happens to the maximum height of each swing? If you attached a sensitive thermometer to the pendulum, what would happen to its temperature as it continued to swing?
- What will be the fate of the pendulum? What kind of energy will it have at that time?
- How does the conservation of energy apply to this situation?
- A constant force propels a rocket ship through space.
- Describe the resulting speed and acceleration of the rocket ship.
- Is there a limit to how fast the rocket ship can go? If so, what is it?
- What is the relationship between mass and energy? What happens to the energy transferred to the rocket ship at high speeds?
- What effect does this have on the rocket ship's acceleration?
- Explain how pressing on the nozzle of a Ready Whip container releases the whipped cream. What type of energy does the compressed carbon dioxide have?