Video Review
Key Concept Summary
TA Summary
Vocabulary
A subdivision of geologic time. Smaller than an era, it is usually several tens of millions of years long.
A type of radioactive decay clock that uses the trails of tracks created by uranium fission decay to determine the age of geologic events
Determining the sequence in which events occurred relative to each other.
The largest subdivision of geologic time.
A chart that breaks down geologic time according to the animals and plants that were found in each division.
A break in the earth where rocks on one side of the break have slipped past the rocks on the other side.
A numeric or quantitative measure of time.
The idea that the laws of nature do not change with time.
The time required for half of the parent isotope to decay to the daughter isotope.
A common animal with a segmented body that lived in the Earth's oceans during the Paleozoic Era.
Igneous rocks that are pushed upward through surrounding layers of rock.
An extinct group of paleozoic sea creatures that had shells.
A break or gap in the geologic record often caused by erosion.
A section of rock that is completely surrounded by a different type of rock.
A boundary where one rock's layers are abruptly interrupted, typically by a fault or another type of rock.
True/False
Our best estimate for the age of the Earth is 4.6 million years.
The principle of superposition lets us determine the absolute ages of layers in a stack of sedimentary rocks.
Daughter isotopes are the products of decay of radioactive elements.
Half-life is the time it takes for one-half of the atoms of the radioactive parent isotope to decay.
An era is a smaller subdivision of geologic time than a period.
Uniformitarianism says that the same geologic processes occurring today in an particular location on Earth occurred in the same places in the past.
Analysis
Which of the following principles is not used in relative dating?
A sedimentary rock layer lies on top of a lava flow. The lava flow has been dated at 44 million years. Both the sedimentary rock layer and the lava flow are cross-cut by a dike of igneous rock that has been dated at 27 million years. The layer of sedimentary rock has an age of
To be useful as geologic clocks, radioactive isotopes must occur in
A fault that cuts through a group of sedimentary rock layers is
Uranium-238 has a half-life of 4.5 billion years. If a mineral has 200 uranium atoms when it is forms, about how many of these atoms would be left after 9 billion years?
A moon rock contains equal amounts of uranium-238 and its decay products. How many half-lives have gone by since the rock solidified?
Which of the following is the determination of ages in years?
When you date a rock using radiometric dating, what does the number actually mean?
According to scientists, the Earth is approximately how old?
Which of the following are used to estimate the age of rocks?
If layers of Rock A cut across layers of Rock B, which of the rock layers is oldest?
In the picture below, rock A is radiometrically dated at 37 million years. What can you conclude? 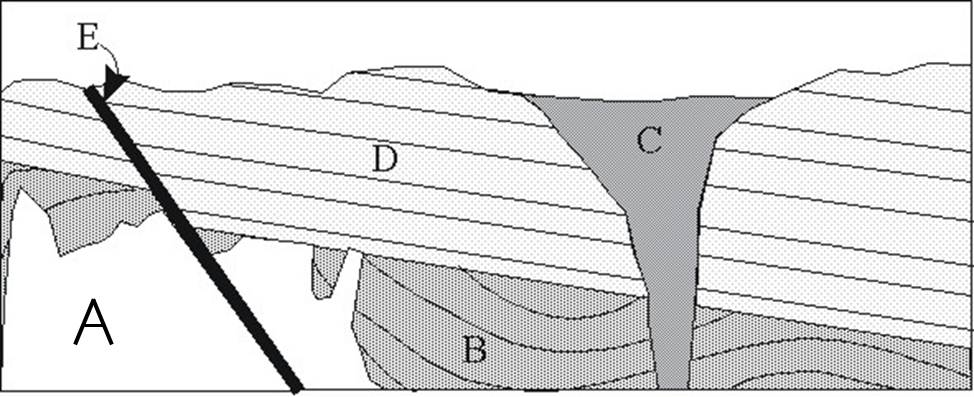

If the half-life of potassium-40 is 1.6 billion years, how much of the original amount of potassium-40 in the sample would remain after 3.2 billion years?
Referring to the photograph below, Rocks A and B represent rocks of any kind. Which of the following statements is true? 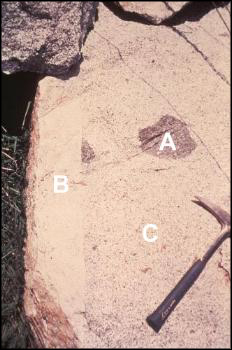

Which of the following is one of the relative dating principles?
In the picture below, what is the correct order of layers from oldest to youngest? 

Refer to the figure below. Which of the following lists has the rocks ordered from oldest to youngest?(E is a fault, not a rock) 
